The leaf is the main photosynthetic organ of the plant, and it is also the main way for transpiration. The size of its area has a significant impact on its own growth and development, light energy utilization, dry matter accumulation, yield and economic benefits. The size of the leaf area is an important parameter for studying crop growth and development, population photosynthetic efficiency and developing crop cultivation measures and technical standards. The determination of leaf area is an indispensable basic skill in plant growth analysis methods.
There are many methods for measuring the leaf area of ​​crops, which can be divided into two major categories, namely traditional methods and modern methods. The traditional leaf area determination methods mainly include the gravimetric method, and a variety of specific measurement methods have been developed based on the principle that the area and mass of the homogeneous material are proportional. Its fineness, accuracy and speed are the biggest features. However, modern methods have affected the popularity due to the fact that instruments such as living leaf area meters are expensive, inconvenient for field measurements, insensitive photocells, and high technical requirements. Relatively speaking, the traditional method for measuring leaf area has the advantages of simple equipment requirements and low technical requirements, and each characteristic and applicable range still has wide application value.
In the traditional method, the length-width-dimension method refers to the method of measuring the maximum length and the maximum width of the tested blade with a ruler, and the method of obtaining the leaf area by multiplying the product of length and breadth and multiplying the correction coefficient k; the regression analysis method based on the coefficient method It is simple and quick. The precondition for these two methods is that the coefficients used must be determined by other methods before they can be used, and the estimation coefficients will differ depending on the crop type, variety, and reproductive status. The biggest advantage of these two methods is that they can be determined by live strains and fixed sites without damaging the plants. In the case of fewer or more precious materials, these two methods are more practical and unique. The discussion of the two methods in potato leaf area determination is now discussed for reference.
Calculation of plant leaf area coefficient K 2.1.1 Measured long Li, wide Ni, and long-width product Si values ​​were measured within 5 plots and the length of 50 leaves was measured with a straightedge Li (from leaf base to leaf) Tip, not including petiole, and leaf width Ni (the widest point in the direction perpendicular to the main vein on the blade). The measurement results are shown in Table 1. The product Si′ of the length and width is calculated, that is, Si′=Li×Ni. The calculation results are shown in Table 2.
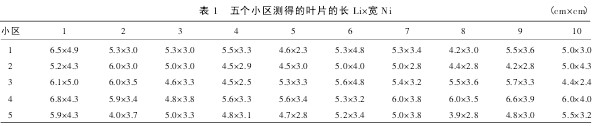
Table 1 Long Li×wide Ni of the blade measured in five plots
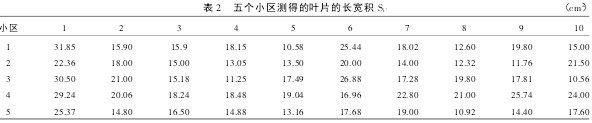
Table 2 The length and breadth product of the leaf measured in five plots
Paper-cut weighing method to determine the actual leaf area of ​​the plant will be selected leaf sample according to its actual shape and size, with the same quality paper cut into paper mold.
All leaf molds were placed in an oven at 60°C for 12 hours to remove water from the paper. After cooling, the paper molds were individually weighed using an electronic analytical balance (FA1604, 0.000 1 g) to yield 50 paper mold weights Wi (Table 3).
The approximate leaf area of ​​the plants determined by the coefficient method was measured and calculated. See Table 4 for the data of standard paper samples and paper molds used in the tests. The actual leaf area Sa (cm2) can be obtained from Table 3 and Table 4. Then, calculate the approximate area Sb based on the data in Table 2, divide Sa by Sb, calculate the correction coefficient k, denoted as k=Sa/Sb, obtain k as 0.726 4, multiply the length and width product of each leaf by k, the leaf area estimated by the coefficient method for each leaf was obtained.
Establishment and Significant Analysis of the Regression Equation Between Leaf Area and Each Factor
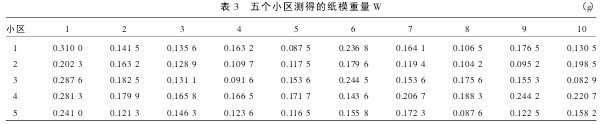
Table 3 Weights of paper molds measured in five plots
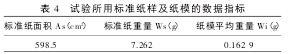
Table 4 Data indexes of standard paper samples and paper molds used in the experiment: Potato leaf length (x1), leaf width (x2), and leaf length×leaf width are the main parameters, and a regression equation with leaf area (y) is established. y=ax+ b. The calculation results are shown in Table 5. From Table 5, the correlation coefficients between leaf length, leaf width, and leaf area were 0.915 2 and 0.946, respectively, and the leaf length and the multiple correlation coefficient between leaf width and leaf area were 0.986 8. Both were significant at the 0.01 level. Sex. All three regression equations can be used to calculate the leaf area of ​​potato. The regression equation with leaf length × leaf width and leaf area is the most accurate, the leaf width is the second, and the leaf length is relatively poor.
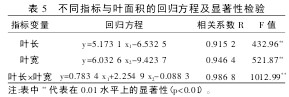
Table 5 Regression equations of different indicators and leaf area and significance test The correlation coefficient of the regression equation is greater than the critical value of the correlation coefficient test, reaching a very significant level. It can be seen that using this method to simulate the calculation of leaf area has a very strong correlation and good results.
This test only measured potato varieties in the Atlantic Ocean. The correction factor for leaf area by long-width-dimension method was 0.726 4. The suitability of other varieties remains to be determined by further experiments. The coefficients a and b in the regression equation method vary with potato varieties, and need to be determined experimentally as well.
Leaf length, leaf width, leaf length × leaf width, and leaf area showed highly significant positive correlations. The correlation coefficients and multiple correlation coefficients were 0.915 2, 0.946 4, 0.986 8, and the one-variable regression equations were extremely significant. At the level, all three regression equations can be used as a regression equation to estimate potato leaf area. In the specific application, it can be selected according to the required accuracy. Using the first two regression equations to determine the potato leaf area can save 50% of the workload, in which the regression equation of leaf width and leaf area is more accurate. If the precision requirement is high, the regression equation of leaf length × leaf width and leaf area can be selected. In general qualitative determination, the regression equation of leaf width and leaf area or leaf length and leaf area can be selected for estimation.
Coefficient method and regression equation method are two methods for estimating leaf area without damage. Compared with gravimetric method, leaf area instrument method, grid method and other measurement methods, they are simple, fast, and non-invasive. They are two kinds of comparison. Good live plants to determine potato leaf area. In practice, only the leaf width or leaf length is measured, which greatly saves the measurement time.
VTM Disposable Virus Sampling Kit
Oral Swab,Nasal Swab,Virus Sampling Tube,Virus Transport Medium
ZSL MED , https://www.zslmed.com